How LEDs Work and What are the Basic Principles of Their Technology?
LED stands for Light Emitting Diode. It is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current passes through it. Unlike traditional light bulbs, LEDs do not rely on heated filaments. Instead, electrons move through a semiconductor material to produce light directly, a process called electroluminescence.
This method makes LEDs more efficient, durable, and adaptable. That's why they're used everywhere, from indicator lights to huge digital panels and electronic scoreboards.
Inside an LED: How Light is Produced
An LED has two layers, one with a positive charge (p-type) and the other with a negative charge (n-type). When current flows through the junction between these layers, electrons move through the space between them and release energy in the form of light.
The color of the light depends on the semiconductor material used. For example, gallium arsenide emits red light, while indium gallium nitride produces blue or green light. By combining these colors, manufacturers can produce color displays.

Why are LEDs more efficient?
LEDs use energy more efficiently because they convert almost all electricity into light, not heat. Traditional light bulbs waste a lot of energy in the form of heat, which reduces their lifespan.
This efficiency is one of the main reasons why LEDs dominate modern lighting systems and displays. For example, a large electronic scoreboard LED lighting can remain bright and clear for hours using far less energy than older lighting technologies.
The Role of Pixels in LED Screens
In LED displays, each pixel is composed of tiny light sources: red, green, and blue LEDs. When these three colors combine, they produce millions of shades, creating vivid and detailed images.
THE pixel density Pixel density determines the sharpness of an image. A higher pixel density means more LEDs concentrated in a specific area, resulting in sharper images. This is why LED screens for indoor environments use a smaller pixel spacing than screens for outdoor environments, which are viewed from a greater distance.
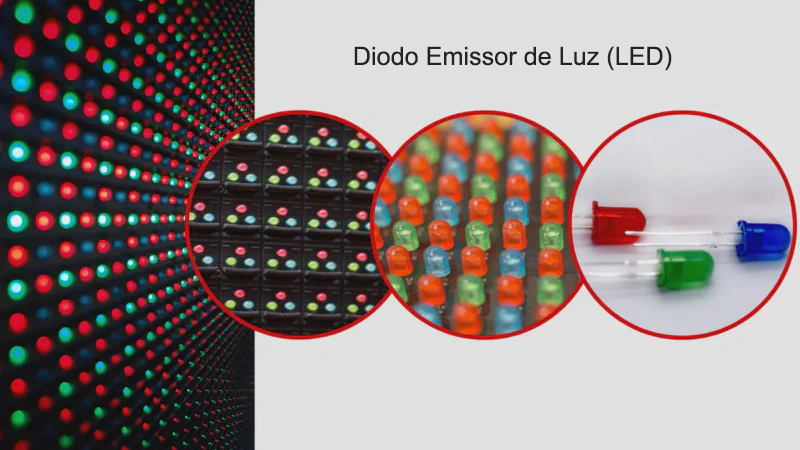
How LEDs Create Images and Videos
LED screens do not display images like a monitor Instead, they use control systems to switch specific LEDs on and off at high speed, forming patterns of light and color. This rapid switching creates moving images when viewed by the human eye. The brightness and color of each LED can be adjusted independently, allowing the screens to display anything from simple text to complex animations or videos.
Types of LEDs Used in Displays
There are several types of LEDs used in the manufacture of displays:
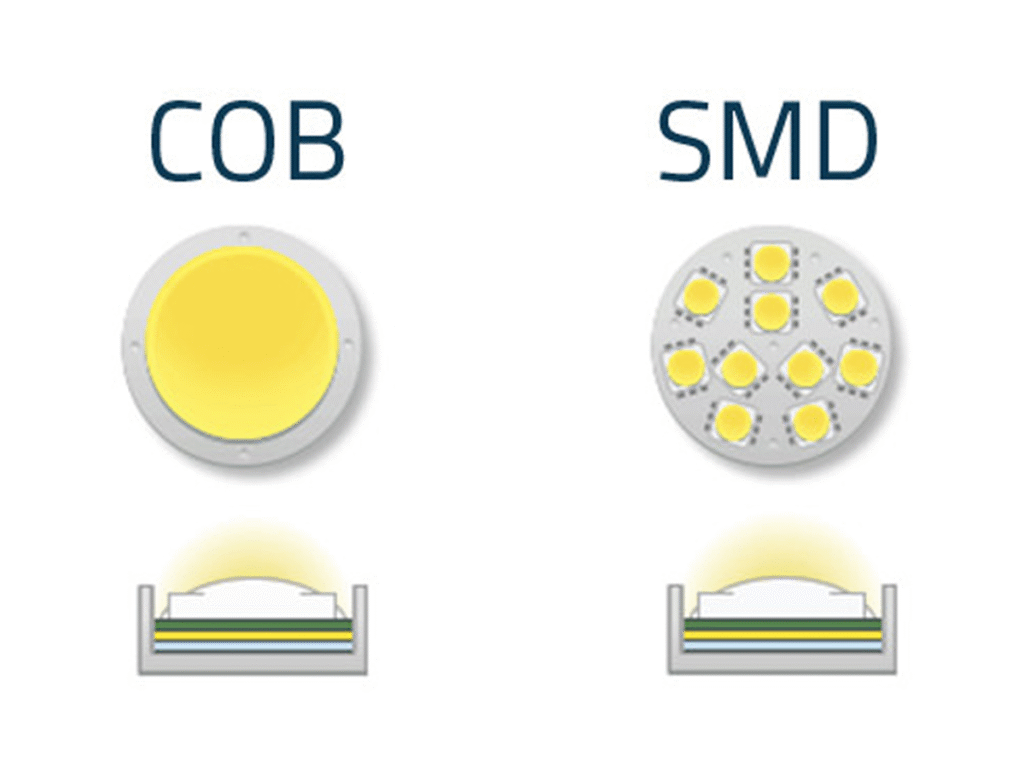
- SMD (Surface Mount Device): Compact LEDs mounted directly onto printed circuit boards, perfect for indoor displays and close-up viewing.
- DIP (Dual-in-Line Package): More durable and brighter traditional LEDs, ideal for outdoor use.
- COB (Chip-on-Board): Advanced LEDs with high uniformity and brightness, offering better color mixing and reliability.
Each type has its advantages, depending on the installation environment and viewing distance.
The Advantages of LED Displays
Displays are popular for several reasons:
- ShineThey remain visible even in direct sunlight.
- Longevity: High-quality LEDs last tens of thousands of hours with minimal maintenance.
- Flexibility: They can be built in different sizes and shapes, from flat panels to curved screens or transparent.
- Energy savingThe reduction of energy consumption It reduces costs in the long run.
These advantages make LEDs the ideal choice for modern digital signage, retail displays, and electronic scoreboards.
Common Applications of LED Technology
Today, LEDs are used in virtually every field of visual communication. You'll find them in advertising billboards, event backdrops, stage lighting, and public information displays.
They are also essential in sports arenas, where LED electronic scoreboards provide real-time updates and replays.
Manufacturers such as LED screen They specialize in building durable, high-performance LED systems designed for indoor and outdoor use, combining precision engineering with long-term reliability.

The Future of LED Technology
LED innovation continues to evolve. Advancements such as micro LEDs and transparent LED panels are further driving brightness, color accuracy, and design flexibility. The displays of the future will be thinner, lighter, and more efficient, opening up new possibilities for architecture, retail, and entertainment. As technology improves, LEDs will remain at the heart of modern visual solutions—efficient, powerful, and endlessly adaptable.
Final Considerations
To understand LEDs: How they work It provides a better appreciation of the technology behind today's digital displays. From how electrons create light to how pixels form vivid images, every component of an LED system is designed for performance and efficiency. Whether for advertising, sports, or... events, LED technology continues to illuminate the world, a diode one at a time.
