Introduction to diodes and LEDs
In the world of electronics, diodes and light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are essential components that play a crucial role in the design and operation of circuits. Although both are types of semiconductor devices, they serve different purposes and are used in a variety of applications across diverse industries. In this blog, we will explore what diodes and LEDs are, how they work, and the difference between them.
What are diodes?
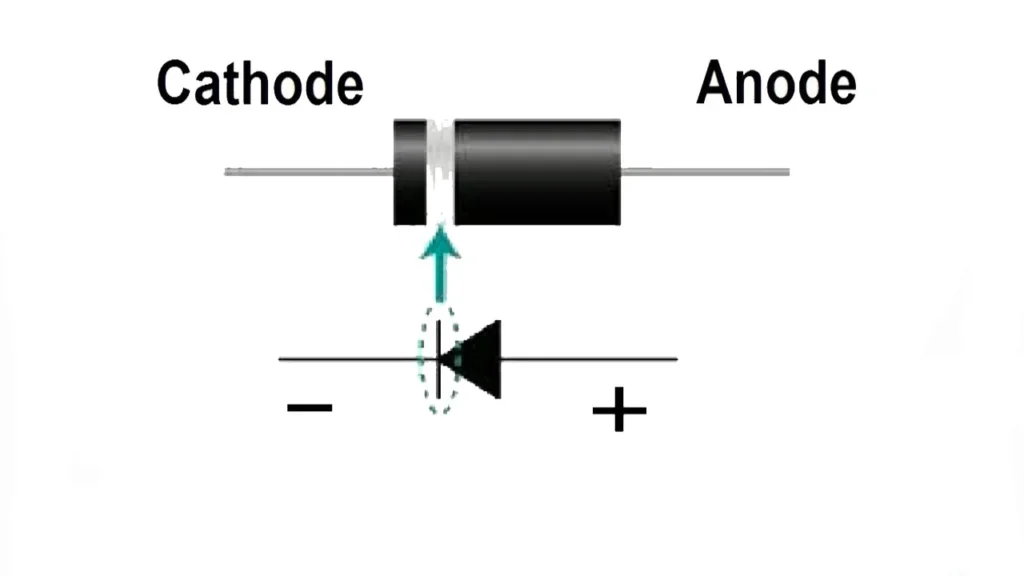
A diode is a semiconductor device that allows current to flow in only one direction. It has two terminals: an anode (positive side) and a cathode (negative side). Diodes are commonly used to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), a process known as rectification. They are crucial in power supplies, signal processing, and radio frequency applications.
How do diodes work?
The operating principle of a diode is based on the properties of semiconductors. When a forward voltage is applied to the diode (anode to cathode), it allows current to pass through. If the voltage is reversed, the diode blocks the current, preventing its flow. This unidirectional behavior is what makes diodes indispensable for ensuring the proper flow of current in electronic circuits.
Common applications of diodes:
- Rectifiers: They convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) in power supplies.
- Zener diodesUsed for voltage regulation in electronic circuits.
- Photosensitive diodes: Found in photovoltaic cells, converting light into electrical energy.
What are LEDs?
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a type of diode that emits light when an electric current passes through it. Unlike ordinary diodes, which simply allow or block the passage of electricity, LEDs convert electrical energy directly into light energy through a process known as electroluminescence. LEDs are widely used in displays, lighting, and indicators due to their energy efficiency, long lifespan, and brightness.
How do LEDs work?
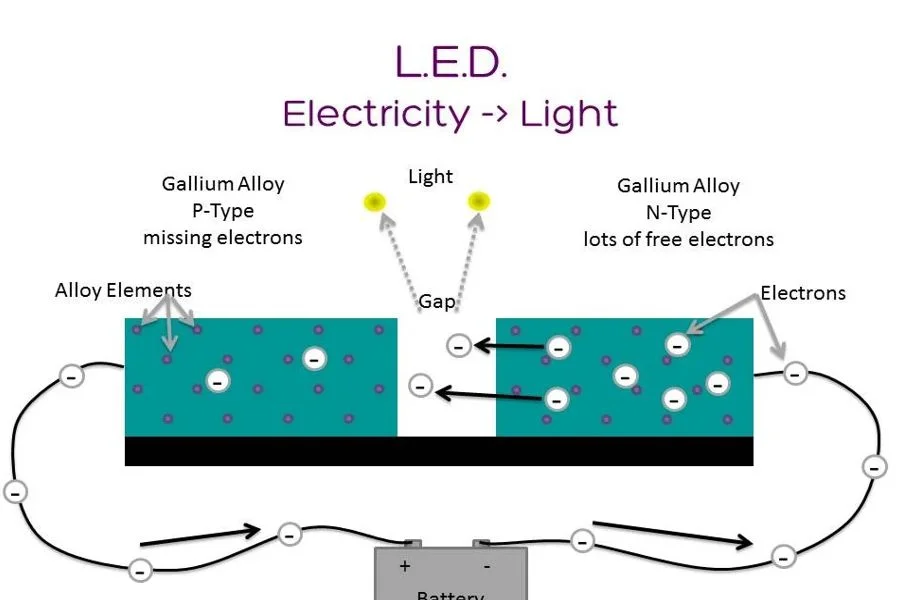
When an electric current flows through an LED, electrons combine with holes in the semiconductor material, releasing energy in the form of photons, which we perceive as light. The color of the emitted light depends on the semiconductor material used in the LED. For example, red LEDs use different materials than blue or white LEDs.
Common applications of LEDs:
- Screens: Found in televisions, smartphones, and monitors.
- Lighting: Energy-efficient light bulbs and decorative lighting
- Indicators: Used in traffic lights, car dashboards, and electronic devices.
Diodes vs. LEDs: Key Differences
| Feature | Diodes | LEDs |
| Main function | It allows current to pass in only one direction. | It emits light when an electric current flows through it. |
| Light emission | It does not emit light. | It emits light through electroluminescence. |
| Applications | Rectification, voltage regulation, signal processing | Lights, displays, indicators |
| Energy efficiency | Moderate | High energy efficiency |
| Useful life | Moderate | Long lasting and durable. |
Why are diodes and LEDs important in modern electronics?
When an electric current flows through an LED, electrons combine with holes in the semiconductor material, releasing energy in the form of photons, which we perceive as light. The color of the emitted light depends on the semiconductor material used in the LED. For example, red LEDs use different materials than blue or white LEDs.
Environmental Impact
One of the significant advantages of LEDs compared to traditional lighting methods (such as incandescent bulbs) is their energy efficiency. LEDs consume less energy and have a much longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste. This makes them a more sustainable option in the fight against environmental degradation.
Technological Advances
Technological advancements have led to the development of specialized types of diodes and LEDs. For example, organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) are a type of LED that enables flexible displays, opening up new possibilities in wearable technology and foldable smartphones. Similarly, laser diodes are used in high-precision applications such as fiber optic communication and barcode readers.
